How to Run a Successful Website Migration Without Losing SEO
Table of Contents
Website migrations—like changing domains, merging subdomains, or re-platforming to a new CMS—can be risky if rushed. Traffic dips, broken links, or mismanaged redirects often cause major SEO losses. Yet migrations can also offer opportunities to refresh structure, fix legacy issues, and enhance performance.
This article guides you through best practices for a smooth website migration that preserves or even boosts search rankings. By planning meticulously, mapping redirects, monitoring post-launch metrics, and addressing user experience details, you’ll reduce downtime and maintain your SEO equity.
“A successful website migration done right can revitalise your site, but ignoring critical steps can sabotage years of SEO gains,” warns Ciaran Connolly, Director of ProfileTree.
Common Reasons for Site Migrations
Website migrations happen for various reasons, from rebranding and platform upgrades to performance improvements and SEO enhancements. Whether shifting to a new CMS, changing domain names, or improving site structure, each migration comes with challenges and opportunities. Understanding the most common reasons for site migrations can help you plan effectively and minimise disruptions.
Domain Changes
A brand rebranding or merging multiple domains under a new umbrella might require a domain switch (e.g., “example2.com” to “example.com”). Properly handling old URLs is crucial to keep link authority intact.
CMS or Platform Migration
Shifting from WordPress to Shopify, or from a custom platform to a modern framework, involves more than just migrating content—it requires careful handling of SEO, user experience, and backend functionality. The site’s URL structure might change drastically, potentially affecting every page’s search rankings and organic traffic. Without a well-planned approach, broken links and lost authority can harm visibility. Thorough audits, redirect mapping, and testing are essential to ensure a seamless transition, preserving rankings and minimising disruptions for users.
Restructuring Site Architecture
Perhaps you’re cleaning up URL hierarchies, removing subdomains (like “blog.example.com” into “example.com/blog”), or reorganising categories. If you handle the transitions well, you can unify link juice and user journeys.
Protocol or SSL Upgrades
Shifting from WordPress to Shopify or a custom platform to a modern framework can drastically alter URL structures, impacting SEO. Without proper planning, broken links and lost rankings may occur. Thorough audits, redirect mapping, and testing are essential to ensure a smooth transition. Additionally, updating internal links and monitoring search performance post-migration helps maintain visibility.
Pre-Migration Audit and Planning
A successful site migration starts with thorough auditing and strategic planning. Assessing your current site’s structure, performance, and SEO health helps identify potential risks and areas for improvement. By mapping out key pages, setting benchmarks, and creating a detailed migration plan, you can ensure a smoother transition while preserving search rankings and user experience.
Crawl Your Current Site
Use tools like Screaming Frog or DeepCrawl to compile a full list of URLs, metadata, internal links, and status codes. This snapshot highlights top-performing pages and flags potential issues, ensuring key elements are preserved and errors are addressed before migration.
Backlink Inventory
Export all inbound links from tools like Ahrefs or Moz. Identify pages with strong external links or high domain authority. These pages must be preserved or redirected meticulously. Losing their link equity can drastically hurt rankings.
Analytics and Rankings Benchmark
Track baseline metrics like traffic, conversions, bounce rates, top landing pages, and keyword rankings. After migration, compare them to detect any dips early. Monitor crucial keywords daily or weekly to catch ranking shifts promptly.
Define URL Mapping
Draft a URL mapping document outlining old URLs → new URLs to ensure a seamless transition. For pages that no longer exist, redirect them to the most relevant equivalent rather than a generic homepage to maintain link equity and user experience. Prioritise high-traffic and high-value pages, and test redirects thoroughly to catch any broken links or incorrect mappings before launch.
“Upfront planning is the bedrock. A detailed URL mapping doc spares you from chaotic fixes once the new site is live,” advises Ciaran Connolly.
Executing the Technical Migration
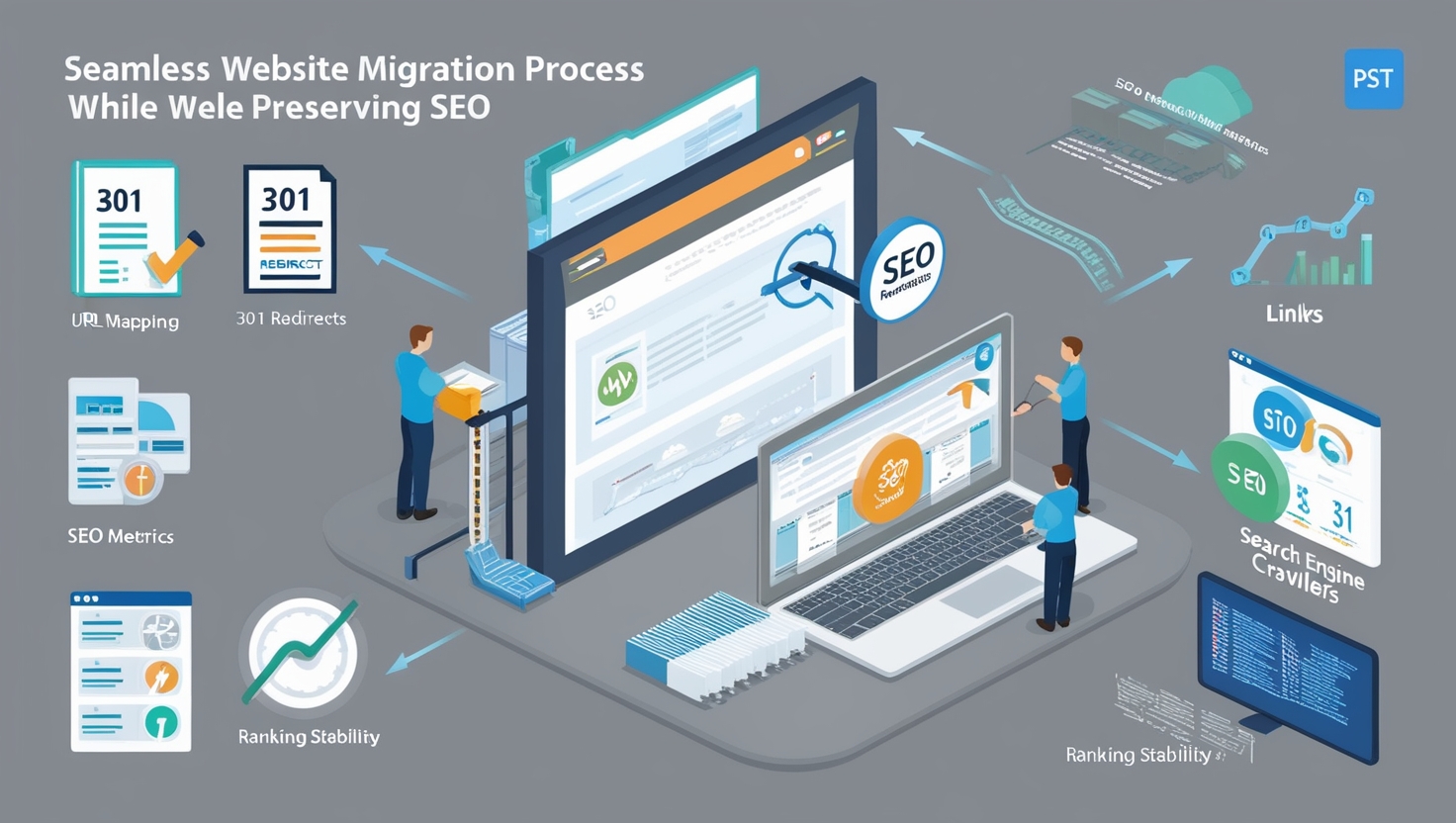
Executing the technical migration requires precision to ensure minimal disruption. This phase involves implementing redirects, updating DNS settings, and transferring content while maintaining SEO integrity. Rigorous testing is essential to catch any broken links, missing assets, or functionality issues. A well-structured approach helps ensure a seamless transition for both users and search engines.
Staging Environment Setup
Don’t attempt major changes on a live site. Create a staging site replicating your environment. Test everything: theme, plugins, new architecture. Ensure SEO-critical elements—like canonical tags, meta data—are present. Then you can fix issues before flipping the switch.
301 Redirects Implementation
301 signals a permanent move, preserving link equity. For each old URL, implement a precise 301 to its corresponding new URL. Tools differ: in WordPress, a plugin like Redirection can handle it, or you can edit server config (like Apache .htaccess). Double-check no redirect loops or chains exist.
Update Internal Links
If your site architecture changes, update hard-coded internal links to point directly to the new structure, rather than relying on chain redirects. Excessive redirects can slow down page loads and dilute link equity, potentially impacting SEO. A clean internal linking structure improves user navigation, ensures search engines can crawl efficiently, and minimises the risk of broken or outdated links.
Managing Canonical and Hreflang
If you have multi-regional sites, ensure any hreflang tags remain consistent under the new URL scheme. Likewise, canonical tags referencing the correct final URLs prevent duplicate content issues. Failing to update these might cause Google to ignore or misunderstand your new pages.
Handling Query Parameters
If your e-commerce site relies on URL parameters (e.g., ?product_id=123), ensure they are correctly handled post-migration. If transitioning from query-based URLs to SEO-friendly paths, implement rewrite rules or canonical tags to prevent duplicate content issues. Keeping a detailed log of parameter-based links in your 301 redirect plan helps maintain search rankings and ensures users land on the correct product pages.
Post-Launch Testing and Monitoring
Post-launch testing and monitoring are crucial to ensuring a smooth transition after migration. This phase involves checking for broken links, verifying redirects, and monitoring site performance, speed, and SEO rankings. Regular audits help identify and resolve any unexpected issues. Tracking user behaviour and engagement metrics also ensures a seamless experience, allowing for quick adjustments if needed.
Immediate Checks
After the new site goes live, conduct a full site crawl to identify 404 errors, misdirected links, or pages with outdated references. Pay special attention to high-traffic and conversion-critical pages. Additionally, test key user interactions—such as sign-ups, checkout processes, and contact forms—to ensure seamless functionality and prevent potential disruptions to the user experience.
Search Console Updates
Add and verify your new domain or property in Google Search Console (and the old one if not done). Submit the new XML sitemap. Monitor coverage and indexation reports for anomalies—like a surge in “excluded” pages or blocked resources. Use the “Change of Address” tool if you moved domains entirely.
Analytics Tracking
Ensure your analytics tool (like Google Analytics or Matomo) is correctly installed on the new site. If domain changes cause a new property or view, set up consistent goals, filters, and e-commerce tracking. Keep an eye on real-time or day-one data to catch major dips quickly.
Backlink Reclamation
Check if external sites updated their links or if you need to request them to link to the new domain/URL. Usually, 301 redirects handle it, but big partner sites or affiliates might prefer direct new links. Some publications or directories might re-check your listing upon request.
Managing Potential Ranking Fluctuations

Ranking fluctuations are common after a site migration, but proactive management can minimise their impact. Monitor search engine indexing, check for crawl errors, and ensure redirects are correctly implemented. Keep an eye on key SEO metrics, such as organic traffic and keyword rankings, to identify any drops early. Updating sitemaps, maintaining high-quality content, and earning fresh backlinks can help stabilise rankings over time.
Anticipate Temporary Drops
Search engines need time to reprocess your site after migration, often causing temporary ranking fluctuations. While minor shifts are normal within the first 1–3 weeks, monitoring daily rankings helps spot unusual trends. Stay patient, but if rankings don’t stabilise after a month or show significant declines, conduct a deeper analysis to identify potential issues like redirect errors, missing metadata, or crawlability problems.
Speed and Performance
A migration often involves hosting changes or architectural shifts that can impact performance. Any slowdown can increase bounce rates and harm user experience, while improvements can enhance engagement. Test load times before and after migration to ensure the new setup is at least as fast—if not faster. Since page speed affects Core Web Vitals, optimising it helps maintain both SEO rankings and visitor satisfaction.
User Feedback
If visitors complain about broken pages or confusing new layouts, address them quickly. Negative user signals can reduce dwell time or boost bounce rate, lowering SERP positions. A short “We’ve moved!” banner or tutorial for loyal users might help transitions.
“Small fluctuations are normal, but consistent or severe dips are red flags. Act swiftly: re-check redirect logs or indexing issues,” says Ciaran Connolly.
Updating External References and Branding
After a site migration, updating external references is crucial to maintaining traffic and brand consistency. Reach out to partners, affiliates, and directories to update backlinks pointing to your old URLs. Ensure your social media profiles, email signatures, and marketing materials reflect the new domain or structure. Consistent branding across all channels helps reinforce trust and prevents confusion among users.
Social Media Profiles and App Integrations
If your domain changes, update all external references, including social media bios, pinned posts, email signatures, and partner websites. Also, review integrations like Slack bots, chat widgets, and automation tools to ensure they don’t rely on outdated URLs. Overlooking these can lead to broken experiences and missed traffic opportunities.
Business Directories and Citations
For local businesses, revise NAP details on Google Business Profile, Yelp, Bing Places, industry directories. Keep brand consistency. Mismatched domain references might confuse potential customers or hamper local SEO signals.
Email Campaigns
If you use email marketing, update all templates, automation sequences, and signature links to reflect the new URL. For a rebrand, inform your subscribers about the migration through newsletters, highlighting key changes. Encourage them to bookmark the new site and explore its updated structure to maintain engagement.
Offline Materials
Review all printed materials—brochures, business cards, packaging, and promotional items—for outdated URLs. If a full reprint isn’t feasible immediately, consider using stickers, QR codes, or temporary disclaimers to guide users to the new site. Ensuring consistency across digital and physical assets maintains brand credibility and prevents confusion.
Handling Special Content During Migration

Certain types of content—such as user-generated content, dynamic elements, or personalised experiences—require extra attention during migration. Ensure databases, comments, and media files are fully backed up and transferred correctly. For interactive features like forums or e-commerce functionality, conduct thorough testing to prevent disruptions. Additionally, maintain SEO equity by properly redirecting high-value pages and ensuring metadata remains intact.
Blog and Article Archives
Long-standing blogs might contain hundreds of posts, each with backlinks and existing SERP presence. Confirm that every post gets a correct 301 redirect or retains the same slug if possible. Avoid changing slugs unnecessarily if it yields minimal benefit.
User-Generated Content
Forums, comment sections, or community platforms can break or generate stale links if the structure changes. A thorough approach ensures every piece of content remains reachable with minimal friction. Additional redirect rules may be necessary.
Media Embeds
Old embedded images, PDFs, or videos might have absolute URLs. Update references or maintain server-level redirects to ensure embedded resources remain accessible. A single broken image might degrade user trust or hamper page layout.
E-commerce Product URLs
Product pages typically have the strongest link or share impetus. If the product slug changes (like from /item/123 to /product/red-shoes), set 301s carefully. Minimising any change is ideal—some e-commerce platforms let you keep legacy slugs for minimal disruption.
Communication Strategy
A clear communication strategy is essential to keep stakeholders, users, and search engines informed during a site migration. Notify internal teams, customers, and partners about potential downtime or changes in access. Update search engines through sitemaps and request indexing of the new site structure. For external audiences, use blog posts, email newsletters, and social media announcements to ensure a smooth transition and minimise confusion.
Internal Team Alignment
From marketing to customer support, everyone should know the migration timeline and what the new site looks like. Provide a short FAQ on potential issues or new features. This step ensures consistent messaging to customers if they ask about changed URLs.
Customer Notifications
For major domain or structural changes, consider emailing or posting a banner: “We’ve moved our site for a better experience! Update bookmarks, etc.” This fosters transparency, reduces confusion, and invites users to explore new pages. Social media announcements also help.
Partner and Affiliate Outreach
If affiliates link to product pages or if partner blogs reference old content, politely request they update or check your new URLs. This direct approach can preserve link equity. Offer them fresh banners or anchor text suggestions where relevant.
“Proactive communication assures users you’re improving, not disappearing. A short notice can prevent them thinking you went offline,” adds Ciaran Connolly.
Post-Migration Monitoring and Refinement
Post-migration monitoring is crucial to ensure a smooth transition and address any unforeseen issues. Track site performance, rankings, and user behaviour using analytics tools to identify dips in traffic or functionality gaps. Regularly check for broken links, crawl errors, and indexing issues. Gather user feedback and adjust content, navigation, or technical aspects as needed. Continuous refinement helps stabilise rankings and ensures an optimised user experience on the new site.
Watch Search Console Errors
If a bunch of new “404 Not Found” or “Soft 404” pages pop up, investigate. Possibly some old URLs missed a redirect, or a dynamic script generated invalid links. Prompt fixes maintain a healthy index.
Compare Baseline Stats
Recall your pre-migration analytics or ranking benchmarks. Are you near or surpassing them after a few weeks? If not, zero in on suspect areas: pages that lost traffic, redirect loops, or speed changes. Minor adjustments can recapture lost ground.
Performance Tweaks
Sometimes migrations come with new code or design. Over time, refine CSS or script loading, ensure mobile performance remains strong. A minor oversight might hamper page speed or user flow—regular checks keep improvements on track.
Gather Feedback
Encourage user comments or an optional “How was your experience on our new site?” quick poll. Real visitors might highlight overlooked issues or confusion. Promptly addressing them fosters loyalty and maintains a brand’s positive impression.
A Successful Website Migration Protects Your Hard-Earned SEO
Migrating a website—be it domain, CMS, or structural overhaul—inevitably poses risks. However, strategic planning, meticulous redirect mapping, robust testing, and proactive post-launch monitoring minimise disruptions and preserve your SEO equity. By involving key stakeholders, communicating changes, and verifying each stage, you can emerge stronger with an updated, user-friendly site.
In short, a migration doesn’t have to mean losing ground in SERPs or confusing loyal visitors. Approach each step carefully—crawl, plan, redirect, test, monitor—and you’ll likely see stable or improved rankings, more cohesive user journeys, and a foundation that better aligns with your brand’s evolving digital strategy.