AI for Sustainability: Driving Green Innovation
Table of Contents
As awareness of climate change grows, businesses face increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices. Beyond ethical responsibility, going green offers cost savings and brand advantages. However, sustainability can feel like a complex challenge, requiring shifts in operations and resource management. This is where artificial intelligence (AI) is proving to be a game-changer, helping companies implement green solutions more efficiently.
AI is transforming sustainability efforts through data analysis, automation, and predictive modelling. Businesses can now monitor their environmental impact, optimise energy use, and reduce waste with intelligent systems. AI-powered algorithms predict maintenance needs, cutting resource waste, while machine learning improves supply chain logistics to lower emissions. From smart grids enhancing energy efficiency to AI-driven agriculture conserving water, the technology is driving eco-friendly innovation across industries.
In this article, we’ll explore how AI supports sustainability and highlight real-world green innovations. From climate modelling to smart resource management, AI is tackling major environmental challenges. However, responsible integration is crucial—misuse can lead to unintended consequences like high energy consumption or ethical concerns. By understanding AI’s potential and limitations, businesses can harness its power for a greener future.
“Using AI for Sustainability may seem a little odd, but together they form a powerful alliance. Data-driven insights can pinpoint inefficiencies and guide us to more planet-friendly solutions faster than traditional methods,” says Ciaran Connolly, Director of ProfileTree.
The Sustainability Imperative in Business
Sustainability is no longer just a corporate buzzword—it has become a business necessity. With rising consumer expectations, stricter regulations, and increasing environmental risks, companies can no longer afford to overlook their impact on the planet. Over 60% of consumers prefer to buy from brands with clear environmental or social goals, while governments worldwide are imposing stricter regulations. Investors, too, are factoring in sustainability by using Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) metrics to evaluate companies.
As a result, businesses that fail to adopt sustainable practices risk reputational damage, financial penalties, and lost opportunities, while those that embed sustainability into their strategies gain competitive advantages, from cost savings through energy efficiency to stronger brand loyalty and market differentiation.
Beyond regulatory and market pressures, sustainability is crucial for long-term business resilience. Climate change-related disruptions, such as extreme weather events and resource shortages, pose significant operational risks. Companies that proactively reduce their carbon footprint, improve supply chain sustainability, and embrace circular economy principles are better equipped to navigate these challenges. Sustainable innovation not only reduces environmental harm but also enhances profitability by optimising resource use and unlocking new growth opportunities in emerging green markets.
Consequently, businesses can no longer treat sustainability as a superficial add-on—it must be woven into their core strategies.
AI is playing an increasingly vital role in helping businesses meet their sustainability goals. From enhancing energy efficiency and reducing waste to improving environmental monitoring, AI-driven solutions are enabling companies to take smarter, data-driven approaches to sustainability. By integrating AI into their sustainability strategies, businesses can move beyond compliance and make meaningful, scalable progress toward a greener future.
Optimising Energy Usage with AI
One of the most direct applications of AI in sustainability is energy management. Traditional energy-saving measures often rely on static policies, such as scheduled lighting or heating reductions. AI enables more dynamic, real-time, and context-aware approaches to optimising energy consumption, leading to significant efficiency gains across various sectors.
Smart Buildings
AI-powered energy management systems adjust heating, cooling, and lighting based on real-time occupancy and external conditions. For example, if certain meeting rooms remain unused, the system can automatically reduce air conditioning or heating to minimise waste. AI can also anticipate occupant behaviour, preemptively adjusting temperature and lighting levels only when necessary.
Additionally, AI-integrated IoT sensors track energy consumption patterns and suggest optimisations, such as shading adjustments to reduce cooling needs or shifting energy-intensive activities to off-peak hours.
Smart Grids and Renewable Energy Integration
Utility providers use AI to optimise power distribution, balancing supply and demand while integrating renewable energy sources more efficiently. AI predicts peak usage times, shifts loads accordingly, and reduces overall grid strain by dynamically routing power where it is needed most. AI-driven predictive maintenance also helps prevent power outages by identifying faults before they cause disruptions.
Besides, AI enhances the efficiency of renewable energy sources like wind and solar by analysing weather patterns and adjusting energy storage and distribution strategies in real time.
Manufacturing Efficiency
Factories can significantly cut energy consumption using AI-driven automation and analytics. AI helps coordinate machine usage, schedule energy-intensive processes during off-peak hours, and detect inefficiencies or equipment malfunctions. Machine learning models analyse energy data to identify opportunities for reducing electricity, gas, and water consumption.
In some cases, AI-driven optimisations lead to double-digit percentage reductions in energy usage, lowering costs while reducing environmental impact.
AI in Data Centres
As digital services expand, data centres are among the largest consumers of energy. AI-driven cooling and workload distribution systems help reduce energy usage by optimising server performance and airflow management.
Companies like Google and Microsoft use AI to cut data centre cooling costs by analysing historical temperature, workload, and weather data to make real-time adjustments, achieving up to 40% reductions in energy consumption.
AI-Driven Transportation Efficiency
AI optimises energy use in the transportation sector by improving route planning, reducing fuel consumption, and supporting the transition to electric vehicles (EVs). AI-powered fleet management systems analyse traffic patterns, weather conditions, and fuel efficiency data to recommend the most energy-efficient routes. In public transportation, AI adjusts schedules and capacities based on real-time demand, minimising energy waste. Also, AI aids in EV battery management, enhancing charging efficiency and prolonging battery life.
By leveraging AI in these diverse areas, businesses and industries can significantly improve energy efficiency, lower costs, and reduce their carbon footprint. AI’s ability to analyse vast amounts of data, predict trends, and automate energy-saving decisions makes it a crucial tool in the transition toward a more sustainable future.
Reducing Waste and Driving Circular Economy
AI helps identify inefficiencies in supply chains and suggests ways to reuse or repurpose materials, leading to significant reductions in waste and operational costs. Here are some key ways AI is driving waste reduction:
- Predictive Maintenance: Machinery breakdowns lead to wasted energy and raw materials. AI-driven predictive maintenance detects early warning signs (such as unusual vibrations or temperature spikes) and schedules repairs before catastrophic failures occur. This minimises downtime and prevents material waste from unfinished products.
- Smart Recycling: AI-powered computer vision systems sort recyclable materials more accurately and efficiently, preventing contamination. Advanced sorting machines can distinguish between different plastics, metals, and glass on conveyor belts, ensuring higher-quality recycled materials that can be reintegrated into manufacturing.
- Waste Tracking: AI can monitor waste output in real time, analysing production lines, inventory, and disposal bins to pinpoint inefficiencies. In food manufacturing, AI can detect whether certain production runs generate excessive off-cuts, helping businesses refine processes and reduce waste.
- Optimised Packaging Design: AI analyses product packaging and recommends more sustainable materials, lighter-weight designs, or alternative packing methods that use fewer resources. This helps businesses reduce packaging waste without compromising product integrity.
- Supply Chain Optimisation: AI-driven logistics platforms identify inefficiencies in material sourcing, transportation, and inventory management. By reducing overproduction, optimising shipping routes, and minimising excess stock, AI helps lower waste and carbon footprints.
- Material Reuse Suggestions: AI analyses production waste streams and suggests ways to repurpose byproducts. For example, food companies can turn surplus ingredients into secondary products, and manufacturers can find new applications for scrap materials instead of discarding them.
- Demand Forecasting: AI predicts demand more accurately, helping businesses adjust production levels and reduce surplus inventory that might otherwise go to waste. Retailers and manufacturers alike use AI-driven insights to better match supply with actual market needs.
Recent sustainability research shows that AI-driven waste reduction strategies can cut industrial waste by up to 30% and significantly lower operational costs, demonstrating AI’s immense potential in creating more sustainable business practices.
AI for Environmental Monitoring and Conservation
Beyond corporate walls, AI is playing a transformative role in preserving ecosystems and promoting global sustainability. By leveraging machine learning and real-time data analysis, AI helps scientists, policymakers, and industries make informed decisions that protect the environment. Its ability to process vast amounts of data enables better climate forecasting, ecosystem monitoring, and pollution management, all of which contribute to a more sustainable future.
One of the most critical applications of AI is climate modelling. Advanced machine learning algorithms analyse complex climate data, improving the accuracy of weather predictions and long-term climate projections. These insights support governments in disaster preparedness, help businesses assess environmental risks, and shape policies aimed at mitigating climate change. Similarly, biodiversity analysis uses AI-powered drones and remote sensing technologies to monitor wildlife populations, track deforestation, and detect illegal activities such as logging or poaching. By identifying ecosystem changes in real time, AI aids conservationists in protecting endangered species and fragile habitats.
AI also plays a significant role in sustainable agriculture and natural resource management. AI-driven sensors and satellite imaging assess soil health, moisture levels, and crop conditions, enabling farmers to optimise fertiliser use, reduce irrigation waste, and minimise chemical runoff. This leads to better yields while preserving surrounding ecosystems. In marine conservation, ocean health monitoring utilises AI-powered autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) to map coral reef health, detect pollution, and monitor fish populations, providing valuable insights for sustainable fishing and marine protection efforts.
Additionally, AI-driven solutions contribute to land restoration and pollution control. Satellite imagery analysis helps identify degraded land suitable for reforestation or regenerative agriculture, while some AI systems even automate drone-assisted tree planting to accelerate afforestation efforts. AI-enabled sensors track air and water pollution, pinpointing sources of contamination in industrial zones or urban centres. This data allows governments and businesses to implement targeted interventions to reduce emissions and improve public health.
While many of these applications extend beyond typical business operations, they underscore AI’s potential to address large-scale environmental challenges. Companies that invest in or support AI-driven sustainability initiatives—whether through partnerships, sponsorships, or direct implementation—can strengthen their environmental impact while demonstrating a genuine commitment to global sustainability.
Real-World Success Stories
AI is already making a tangible impact on sustainability across industries, from reducing carbon emissions to optimising resource efficiency. Companies and organisations worldwide are leveraging AI to tackle environmental challenges in innovative ways, proving that technology can be a powerful force for positive change. In this section, we’ll explore real-world success stories where AI-driven solutions have led to measurable sustainability improvements, setting a precedent for future green innovation.
Logistics Company’s Fuel Optimisation
A large logistics provider adopted an AI routing tool that not only found the shortest routes but also factored in traffic flow, average speeds, and idle times. By training drivers on the new recommended routes and eco-driving tips, the firm cut fuel consumption by 15% in under a year, significantly lowering their CO₂ emissions. This approach also saved costs on diesel, creating a win-win scenario.
Fashion Retailer’s Predictive Stock Management
A fashion brand faced high waste due to overproduction. By using AI to predict sales volumes and trends more precisely, they reduced overstock by 35%. Unsold clothing and associated environmental costs (fabric, water usage, etc.) fell drastically. Profits improved thanks to fewer clearance sales, and the brand scored better in ethical fashion rankings due to lowered waste.
AI-driven Carbon Accounting
A technology firm developed a tool that automatically tracked every department’s carbon footprint based on utility bills, travel expenses, and supply chain data. The AI flagged “hotspots” of high emissions and recommended areas where green alternatives could be used (e.g., remote conferencing instead of air travel, adopting solar power for a data centre). Over two years, the firm reduced its carbon emissions intensity by 25%, meeting internal ESG targets early.
Overcoming Common Challenges
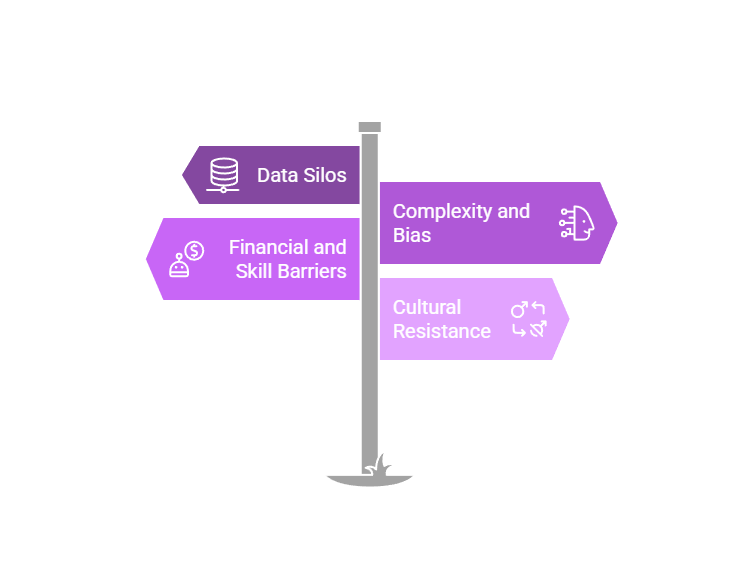
While AI offers immense potential for driving sustainability, its implementation comes with challenges that businesses must address. In this section, we’ll explore common obstacles businesses encounter and practical ways to overcome them, ensuring AI contributes effectively to long-term environmental goals:
- Data Silos: Many businesses keep operational data in separate systems, making it hard to get a full sustainability picture. A consolidated data approach is needed to feed AI effectively.
- Complexity and Bias: Some AI models might oversimplify or produce biased recommendations if they don’t account for all environmental or social impacts. Vigilant oversight is required to ensure AI’s outputs align with genuine green objectives.
- Financial and Skill Barriers: Implementing AI solutions can require upfront investment and staff with data science expertise. Smaller firms might fear these costs, though increasingly, user-friendly AI tools or consultancy support can mitigate this.
- Cultural Resistance: Like any major change, adopting AI for sustainability can face internal pushback – staff might be used to legacy processes or question the reliability of AI forecasts. Effective communication, leadership endorsement, and training ease these transitions.
“For AI to genuinely further sustainability, companies must combine the right data and algorithms with strong ethical guidelines. Otherwise, you risk ‘greenwashing’—appearing eco-friendly on the surface but lacking real substance,” warns Ciaran Connolly.
Roadmap for AI-driven Green Innovation
Integrating AI into sustainability efforts is a step-by-step process that begins with clear goal-setting and evolves through data analysis, tool selection, employee engagement, and continuous improvement. By following this structured approach, organisations can seamlessly incorporate AI to drive meaningful environmental impact.
The process starts with establishing specific and measurable sustainability goals. Whether the focus is on cutting energy consumption by 20%, reducing material waste by 30%, or lowering carbon emissions per product, having clear objectives ensures that AI solutions align with business priorities
Next, organisations assess where relevant data is stored—such as utility records, production logs, and supply chain reports. By unifying this information, businesses create a solid foundation for AI-driven analysis, enabling accurate predictions and real-time optimisations.
With clear goals and structured data, the next step is choosing AI solutions that match the organisation’s needs. Some platforms specialise in energy management, while others focus on waste reduction or supply chain efficiency. In some cases, companies may develop custom AI models to address unique sustainability challenges.
Once AI tools are in place, staff must be trained to interpret and act on AI-generated insights. Encouraging employees to collaborate with AI, rather than fear automation, ensures smoother adoption. Highlighting quick wins, such as immediate energy savings, helps build confidence and enthusiasm.
Finally, sustainability efforts require ongoing monitoring and adaptation. Organisations track key metrics to evaluate AI’s effectiveness, adjust strategies as needed, and expand AI-driven initiatives over time. As businesses refine their approach, they can take on more ambitious sustainability projects, continuously improving their environmental impact.
Future Outlook
As AI matures, expect deeper integration with sustainability. One trend is autonomous systems that continuously refine resource usage—imagine an entire factory adjusting machinery settings in real-time based on environmental data. Another is blockchain integration for transparent, tamper-proof recording of supply chain emissions, verified by AI algorithms scanning logs. Government policies may also mandate detailed carbon reporting or reward AI-based green initiatives, further accelerating adoption.
Crucially, consumer pressure remains a driver—future generations want to support businesses that genuinely care for the planet. The companies that proactively deploy AI for sustainable innovation will shape the new standard for environmentally conscious commerce.
Conclusion
AI offers a potent toolkit for bridging economic ambitions with environmental responsibility. By harnessing data-driven insights, businesses can reduce waste, optimise resources, and design more sustainable products or services. This not only fulfils ethical and regulatory expectations but often yields cost and competitive benefits.
If you’re exploring ways to integrate AI into your sustainability journey—whether that’s through energy management, supply chain analytics, or waste reduction solutions—ProfileTree can help. Our digital transformation and AI expertise ensures your green ambitions translate into tangible, data-backed results.
Ready to power your sustainability goals with AI? Book a call with ProfileTree and let us guide you in implementing AI-driven strategies that protect the planet and propel your business forward.