AI Adoption Rates in UK SMEs: 2025 Survey Insights
Table of Contents
Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer just a buzzword—it’s transforming how British and Irish small-to-mid-sized enterprises (SMEs) operate. By 2025, various surveys indicate AI usage among SMEs has surged, thanks to more affordable cloud-based tools like ChatGPT, improved local digital infrastructure, and supportive government policies.
This article collates the latest 2024–2025 surveys and official statistics on AI adoption in UK SMEs, highlighting growth patterns since 2022. We’ll showcase real-life case studies—like how a local accounting firm uses AI for client queries or how an e-commerce site uses ChatGPT for marketing. This data-driven overview will help business owners, policymakers, and consultants gauge AI’s current state in the UK’s SME landscape.
“Watching AI usage spike among UK SMEs is hardly surprising—tools are simpler, cheaper, and the ROI potential is massive,” observes Ciaran Connolly, Director of ProfileTree.
Snapshot of AI Adoption Trends (2022–2025)
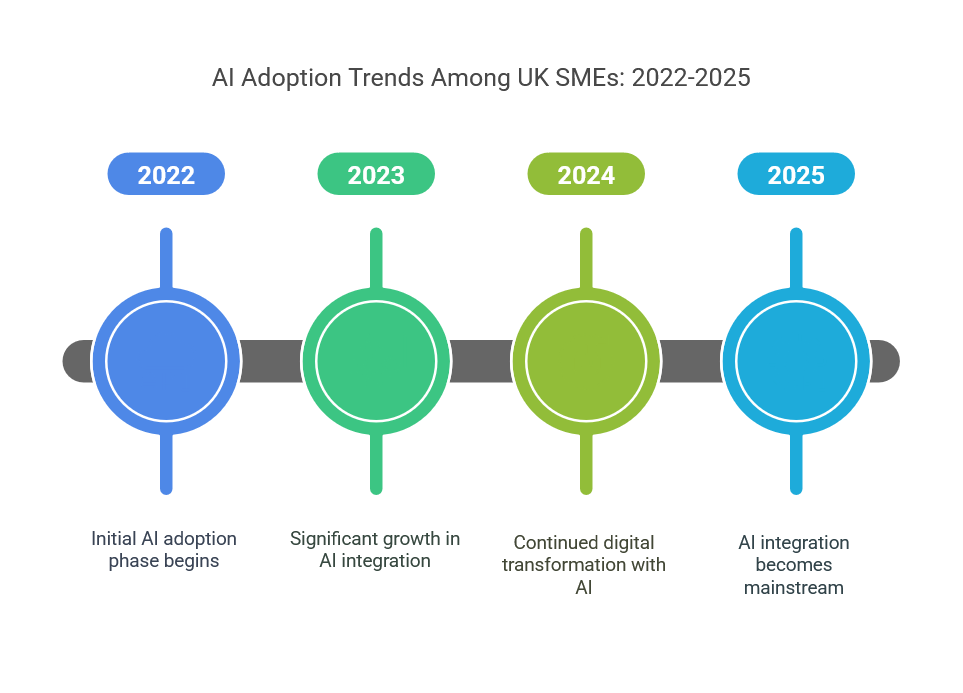
(AI adoption among UK SMEs has rapidly accelerated, driven by technological advancements, increased accessibility of tools, and a shift towards digital transformation. This section provides an overview of AI usage trends from 2022 to 2025, offering insights into the growth of AI integration in businesses across various sectors.
AI Adoption Trends (2022–2025)
Recent surveys and statistics suggest a noticeable increase in AI adoption across UK SMEs:
- 45% of SMEs had integrated at least one AI-based solution by 2024, up from 25% in 2022. This indicates a significant acceleration in AI adoption over the past few years.
- 65% of medium-sized enterprises (50–249 employees) have implemented AI in at least one department, with AI applications ranging from customer service automation to data analytics.
- 30% of micro-businesses (fewer than 10 employees) still hesitate to adopt AI, citing cost and complexity as the main barriers.
- 25% of businesses plan to expand their AI usage in 2025, focusing on automation and data-driven decision-making.
These trends highlight AI’s growing role in UK SMEs, with businesses across sectors leveraging AI to improve operational efficiency and customer engagement. ates mid-level interest, particularly in finance or tourism hotspots.
Why the Spike in AI Adoption?
The rapid increase in AI adoption among UK SMEs can be attributed to several key factors, including the affordability of cloud-based tools, enhanced digital infrastructure, and the growing recognition of AI’s potential to improve business efficiency and customer experience. This section explores the primary reasons behind the surge in AI usage.
Lower Cost, Easier Tools
Previous AI solutions demanded large budgets and specialists. Cloud-based or SaaS AI (like ChatGPT, Google’s Vertex AI, or Azure Cognitive Services) lets SMEs pay only for usage. No advanced coding or on-prem servers are needed—just an internet connection.
Positive Case Studies
As soon as local businesses see neighbours or competitors thriving with AI (like a competitor’s chatbot offering 24/7 support), they realise the practical ROI. Word-of-mouth success fosters a domino effect of adoption.
Pandemic-Driven Digital Acceleration
COVID-19 forced many SMEs online. Even post-pandemic, that digital pivot hasn’t reversed. AI chatbots handle surplus web queries, while generative content saves staff time. Many businesses found the post-pandemic environment perfect for continuing digital transformations.
“We’ve noticed SMEs no longer ask ‘Should we adopt AI?’ but ‘Which AI tool suits us best?’ That shift is telling,” says Ciaran Connolly.
Real Case Studies: How SMEs Use AI
To better understand the practical applications of AI, this section highlights real-world examples of UK SMEs successfully leveraging AI tools to enhance efficiency, improve customer service, and drive growth across various industries.
Accounting Firm: “Smart Ledger Solutions” (Hypothetical)
A mid-sized London-based accounting firm serving 200+ clients.
- Adopted ChatGPT to draft routine client emails, summarise finance news for newsletters, and parse HMRC updates.
- Freed up ~30% of staff time from these repetitive tasks.
- Also used AI-based OCR to convert client receipts into structured data.
Result: Faster document processing, less admin overhead, and employees focusing on advisory services instead of mundane tasks.
E-commerce Startup: “EcoTrends”
An online retailer specialising in eco-friendly goods.
- Employed an AI product recommendation plugin for cross-selling.
- Deployed a customer service chatbot to handle shipping queries and stock info.
- Observed a 15% boost in average order value, plus a drop in cart abandonment.
Result: Freed the 3-person support team to focus on escalations while the bot handled routine queries 24/7.
Consultancy Agency: “BrightEdge Consulting”
A Manchester-based SME offers HR and management consulting.
- Used generative AI tools to create outline frameworks for client proposals.
- Deployed analytics-based email marketing strategies. AI predicted which leads might respond best to certain topics.
Result: 25% higher proposal turnaround speed, improved lead conversions.
ChatGPT in Business: Common Use Cases
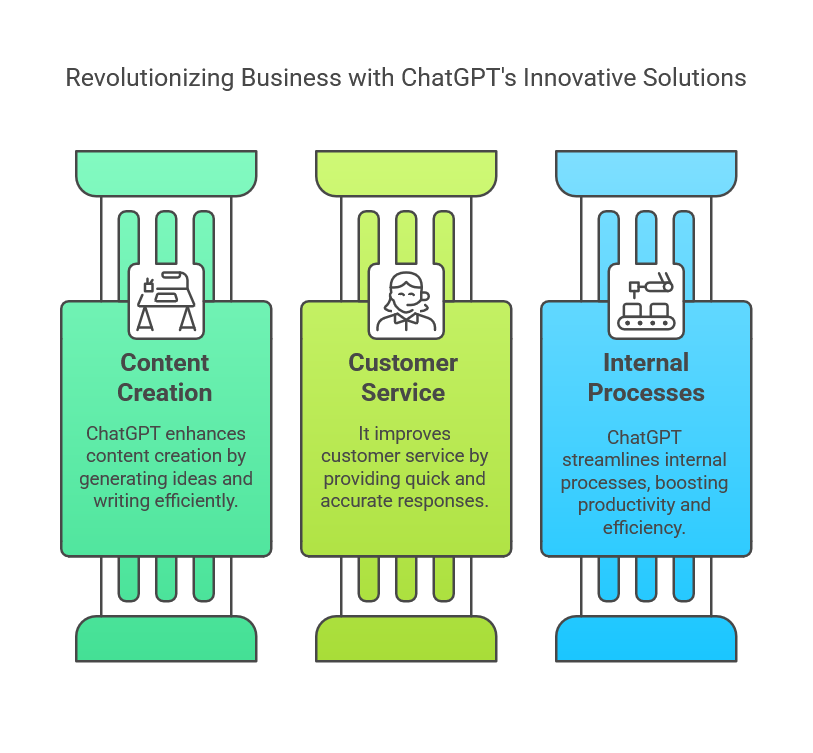
ChatGPT is transforming business operations by streamlining tasks and improving customer interactions. This section outlines how businesses use ChatGPT to enhance content creation, customer service, and internal processes.
Content Generation at Scale
SMEs often lack dedicated copywriting staff. ChatGPT can draft blog outlines, product pages, or social posts. Staff do a final pass, ensuring local tone, compliance, and brand alignment.
Customer Service Chatbots
Many 2025-era chatbots use a GPT-based language model to handle user queries more smoothly than older, rule-based systems. They can recall conversation context, giving more natural replies. This is a big advantage for SMEs that can’t afford large call centres.
Data Summaries and Internal FAQs
ChatGPT can synthesise internal documents and highlight key points for staff who might not have time to read complete manuals. Some SMEs use private ChatGPT instances with strict data constraints for staff knowledge bases.
Practical Guide: Implementing AI Chatbots for Irish Customer Service
This guide provides practical steps for implementing AI chatbots in customer service, focusing on the Irish market. The strategies outlined are also applicable to businesses in the UK, helping SMEs enhance customer interactions and operational efficiency through AI-driven solutions.
Scoping the Project
- Identify Frequent Queries: Shipping times, product specs, booking availability, returns policy.
- Choose a Chatbot Platform: Off-the-shelf solutions with GPT integration vs. custom build with an Irish AI vendor.
- Data and Integration: Ensure the bot can fetch up-to-date stock info from your e-commerce system. Or if in hospitality, it links to your booking system.
Costs and Benefits
A basic AI-powered bot subscription might range from €50 to €300 monthly, depending on usage volume. Implementation might cost an initial consulting fee. But if it cuts 50% of routine calls/emails, staff can handle complex queries or expansions.
ROI: If your staff typically handle 200 queries/week, halving that saves hours of labour. Over time, you might reassign staff to revenue-generating tasks (like upselling services).
Local Success Stories
- A Cork-based B&B added an AI chatbot that answered queries about room availability, location details, and local event suggestions. The owners said phone calls fell by 40%, but overall reservations grew—visitors found info instantly, building trust for direct booking.
- A Dublin fashion retailer integrated a chatbot for sizing queries and product returns. Over three months, the average response time dropped from hours to instant, improving buyer satisfaction.
Overcoming Skill Gaps
Some Irish SMEs worry they lack IT staff. Many chatbot solutions offer no-code setups. Alternatively, hire a local consultant for initial training. The key is instructing staff to maintain the “knowledge base” so the bot remains updated on seasonal products, shipping changes, or new events.
Addressing Data Privacy: GDPR and Ethical Concerns
As AI tools become increasingly integrated into business operations, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR is crucial. This section explores the importance of data protection and the ethical considerations SMEs must address when adopting AI solutions.
GDPR Overview
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) affects how businesses collect, store, and process personal data. For AI, if you feed user data into a model, you must have consent or a lawful basis. If you use ChatGPT, you might risk transferring data outside the EEA if you are not careful.
Minimising Data Exposure
- Anonymise or remove personal identifiers before feeding text into AI tools.
- For chatbots, consider an on-prem or EU-based solution that meets GDPR.
- Provide clear disclaimers if a bot processes personal info, e.g., user queries about account details.
Ethical AI Considerations
- Bias: Large language models can reflect societal biases. To take a fair approach, monitor your chatbot or content generation for discriminatory language.
- Accuracy: ChatGPT can “hallucinate.” SME staff must double-check outputs, especially if decisions involve high stakes (financial advice, legal disclaimers).
“GDPR compliance is crucial in the UK/EU environment. SMEs must ensure AI usage doesn’t breach user trust or legal obligations,” says Ciaran Connolly.
“Navigating AI and GDPR in Ireland: 6 Pitfalls to Avoid”
This section highlights six common pitfalls SMEs may encounter when integrating AI with GDPR compliance in Ireland. By understanding and avoiding these challenges, businesses can ensure their AI solutions remain legally sound and ethically responsible.
Pitfall #1: Collecting Personal Data Without Proper Consent
If your AI chatbot logs user email or sensitive info, you must request permission and detail usage in your privacy policy.
Pitfall #2: Storing Data Indefinitely
AI training sets can accumulate large data sets. GDPR requires the storage of personal data only for as long as necessary. Implement automatic purges or anonymisation.
Pitfall #3: Failing to Assess Third-Party Tools
If you use a US-based AI service, check if it complies with the EU-US Data Privacy Framework or has standard contractual clauses. As a data controller, you remain accountable.
Pitfall #4: Lack of Human Oversight
Users must have recourse to a human if AI-based decisions affect them significantly (like loan approvals). Ensure a channel for human review, fulfilling GDPR’s fairness principle.
Pitfall #5: Not Doing DPIAs (Data Protection Impact Assessments)
Do a DPIA to identify risks for major AI deployments, e.g., storing sensitive user info and potential reidentification. Document how you mitigate them.
Pitfall #6: Overreliance on Automated Decisions
GDPR’s Article 22 restricts fully automated decisions with legal effects unless certain conditions are met (explicit consent necessary for a contract or authorised by law). SMEs adopting advanced AI must ensure user rights to object or request manual review.
Looking Ahead: AI in UK/Irish Business Future
The future of AI in UK and Irish businesses looks promising, with continued advancements in technology and regulation. This section explores the evolving role of AI in business, including emerging trends and opportunities for SMEs in both markets.
Ubiquitous AI Assistants
Within a few years, most SMEs may have an AI assistant or chatbot on their site to handle queries or internal tasks. Over time, that might extend to voice-based systems integrated with popular voice assistants, bridging local user queries with direct brand interactions.
Industry-Specific AI Solutions
As seen in agriculture or tourism, more domAIn-tailored solutions will flourish—like AI for retail stock management or AI for legal document scanning. Ireland/UK-based dev firms might create local-friendly tools that address cultural/language nuances.
Regulatory Evolution
Post-Brexit, the UK might refine its data privacy regime but likely remains close to GDPR for EU trade. Ireland remains a key EU data hub. Expect further guidelines on AI transparency, especially if chatbots or generative content manipulate user decisions or revolve around personal data.
“AI’s normalisation in day-to-day operations will force continuous updates in compliance, usage guidelines, and staff training. Agility remains crucial,” suggests Ciaran Connolly.
Action Plan for Businesses
- Audit Current Processes: Identify admin tasks, marketing workflows, or user queries that consume staff time—these are prime for AI automation.
- Choose Tools Wisely: Evaluate ChatGPT for text, DALL·E for visuals, or local EU-based solutions for better data protection.
- Address GDPR: If personal data is processed, anonymise or ensure relevant consent. Possibly consult a data protection expert.
- Pilot and Measure: Start small, track time saved or conversion lifts, and if the pilot works, scale up.
- Stay Informed: Follow updates from ICO (UK), DPC (Ireland), or relevant government agencies regarding AI compliance or new funding calls.
Embracing AI Responsibly for UK/Irish Businesses
The latest 2024–2025 surveys confirm a strong upward trajectory in AI adoption across Ireland and the UK, especially among SMEs leveraging ChatGPT or advanced analytics. From automated marketing copy to AI chatbots delivering 24/7 customer support, small businesses now harness tools once reserved for large corporations. Yet with potential leaps come challenges: ensuring GDPR compliance, mitigating hallucinations or biases, and guiding staff through the transformation.
Pragmatic strategies—starting with a clear use case, applying for government support, and thoroughly addressing ethical/legal concerns—help SMEs integrate AI effectively. As the British and Irish economies adapt post-Brexit and into a dynamic digital world, AI stands out as a pillar of competitiveness. Done right, it yields faster growth, better user experiences, and a robust future for local enterprises big and small.
Conclusion
The rapid adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) by small-to-medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) across the UK and Ireland is reshaping the business landscape. As tools like ChatGPT become more affordable and easier to integrate, SMEs are seizing the opportunity to automate routine tasks, improve customer service, and enhance marketing efforts, all while saving time and resources. The shift from questioning if AI should be adopted to which AI tools best suit a business’s needs demonstrates the growing confidence in these technologies.
Despite the immense potential, SMEs must remain mindful of challenges such as GDPR compliance, ethical AI use, and staff training to ensure the benefits outweigh the risks. With proper planning, including pilot projects and clear ROI goals, businesses can unlock AI’s transformative power while maintaining legal and ethical standards.
As AI tools continue to evolve and regulations adapt, the role of AI in UK and Irish SMEs will likely expand. Businesses can stay competitive in a rapidly changing digital world by embracing AI responsibly and strategically.
FAQs
u003cstrongu003eWhat types of AI tools are suitable for SMEs?u003c/strongu003e
Some of the most common AI tools for SMEs include chatbots for customer service, generative AI for content creation, predictive analytics for marketing, and AI-powered CRM systems for managing customer relationships.
u003cstrongu003eIs AI expensive to implement for SMEs?u003c/strongu003e
Many AI tools are now affordable for SMEs thanks to cloud-based AI solutions and SaaS models. Pricing typically depends on usage volume and features, with options ranging from basic chatbot subscriptions to advanced data analytics tools.
u003cstrongu003eHow do SMEs ensure AI complies with GDPR?u003c/strongu003e
SMEs can ensure GDPR compliance by anonymising personal data before feeding it into AI models, obtaining explicit user consent, and working with AI providers that offer EU-based data processing. Regular audits and data protection assessments are also critical.